Pharmacology Of Local Anaesthetics
Pharmacology Of Local Anaesthetics. It is aimed at preclinical medical or dental students, or students in the early years of a pharmacology degree. Basic pharmacology of local anaesthetics.
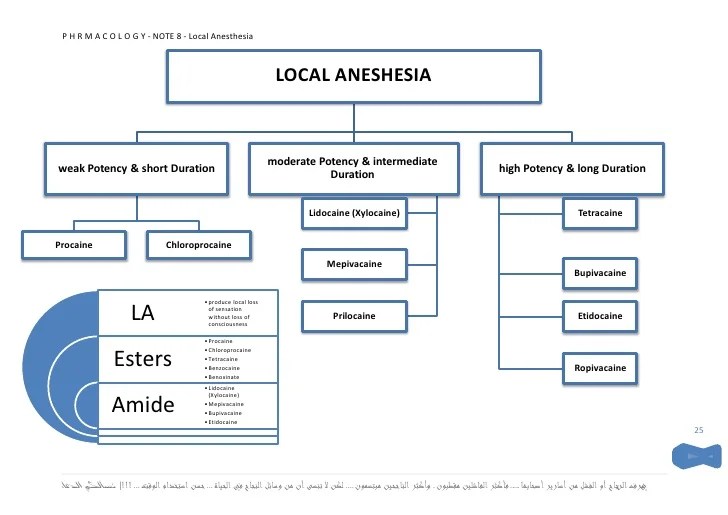
The pharmacology of local anesthetics is an integration of the basic physiology of excitable cells and the mechanism by which local anesthetics are capable of interrupting conduction of neural messages. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The mixture has a additional actions of local anaesthetics lower.
This Is Thought To Occur Via Specific Binding Of The Local Anaesthetic Molecules (In Their Ionised Form) To Sodium Channels, Holding Them In An Inactive State So That No Further Depolarisation Can Occur.
The pharmacology of local anesthetics is an integration of the basic physiology of excitable cells and the mechanism by which local anesthetics are capable of interrupting conduction of neural messages. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Local anaesthetics disrupt ion channel function within the neurone cell membrane preventing the transmission of the neuronal action potential.
The Molecular Structure Of All Local Anesthetics Consists Of 3 Components:
The pharmacology of local anesthetics is an integration of the basic physiology of excitable cells and the mechanism by which local anesthetics are capable of interrupting conduction of neural messages. General properties of local anesthetics. The local anaesthetic molecule consists of 3 components:
Start Studying Pharmacology Of Local Anesthetics.
By definition, the pka is the ph at which 50% of the local anesthetic is uncharged ( [b]= [bh + ]). The eutectic mixture of local anaesthetic (emla) outside the scope of this article. Pharmacokinetics of local anaesthetics in infants and children.
Intrathecal Clonidine As Spinal Anaesthesia Adjuvant — Is There A Magical Dose?
The common characteristics of the molecules with local anesthetic action have been identified and can explain the properties of the agents. The pharmacology of anaesthetics in the neonate. Pharmacology of local anaesthetics and commonly used recipes in clinical practice.
(A) Lipophilic Aromatic Ring, (B) Intermediate Ester Or Amide Chain, And (C) Terminal Amine.
The pharmacology of local anaesthetic agents dr j m tuckley, department of anaesthetics, royal devon and exeter nhs trust classification local anaesthetic agents can be defined as drugs which are used clinically to produce reversible loss of sensation in a circumscribed area of the body. (a) lipophilic aromatic ring, (b) intermediate ester or amide linkage, and (c) tertiary amine. It is aimed at preclinical medical or dental students, or students in the early years of a pharmacology degree.
Post a Comment for "Pharmacology Of Local Anaesthetics"